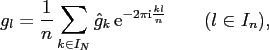Next: The second approximation -
Up: NFFT - nonequispaced fast
Previous: The window function
Contents
Switching from the definition (2.5) to the frequency domain, one obtains
with the discrete Fourier coefficients
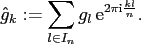 |
(2.6) |
Comparing (2.4) to (2.5) and assuming
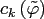 small for
small for
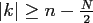 suggests to
set
suggests to
set
![$\displaystyle \hat g_k := \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \frac{\hat f_k}{c_k \left(\...
..._N , \\ [1ex] 0 & \text{for } k \in I_n \backslash I_N . \\ \end{array} \right.$](img99.png) |
(2.7) |
Then the values 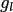 can be obtained from (2.6) by
can be obtained from (2.6) by
a FFT of size 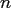 .
.
This approximation causes an aliasing error.
Jens Keiner
2006-11-20