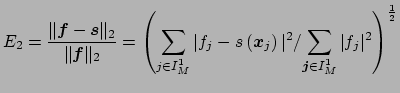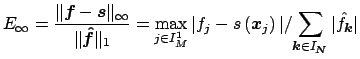Next: CPU-time &
Up: Examples
Previous: Examples
The accuracy of the Algorithm 1, measured by
and
is shown in Figure 3, see ./example/accuracy.
Figure:
The error 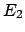 (top) and
(top) and
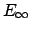 (bottom) with respect to
(bottom) with respect to 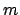 ,
from left to right
,
from left to right 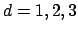 (
(
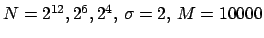 ),
for Kaiser Bessel- (circle), Sinc power- (x), B-Spline- (
),
for Kaiser Bessel- (circle), Sinc power- (x), B-Spline- (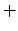 ), and Gaussian window (triangle).
), and Gaussian window (triangle).
|
|
Stefan Kunis
2004-09-03